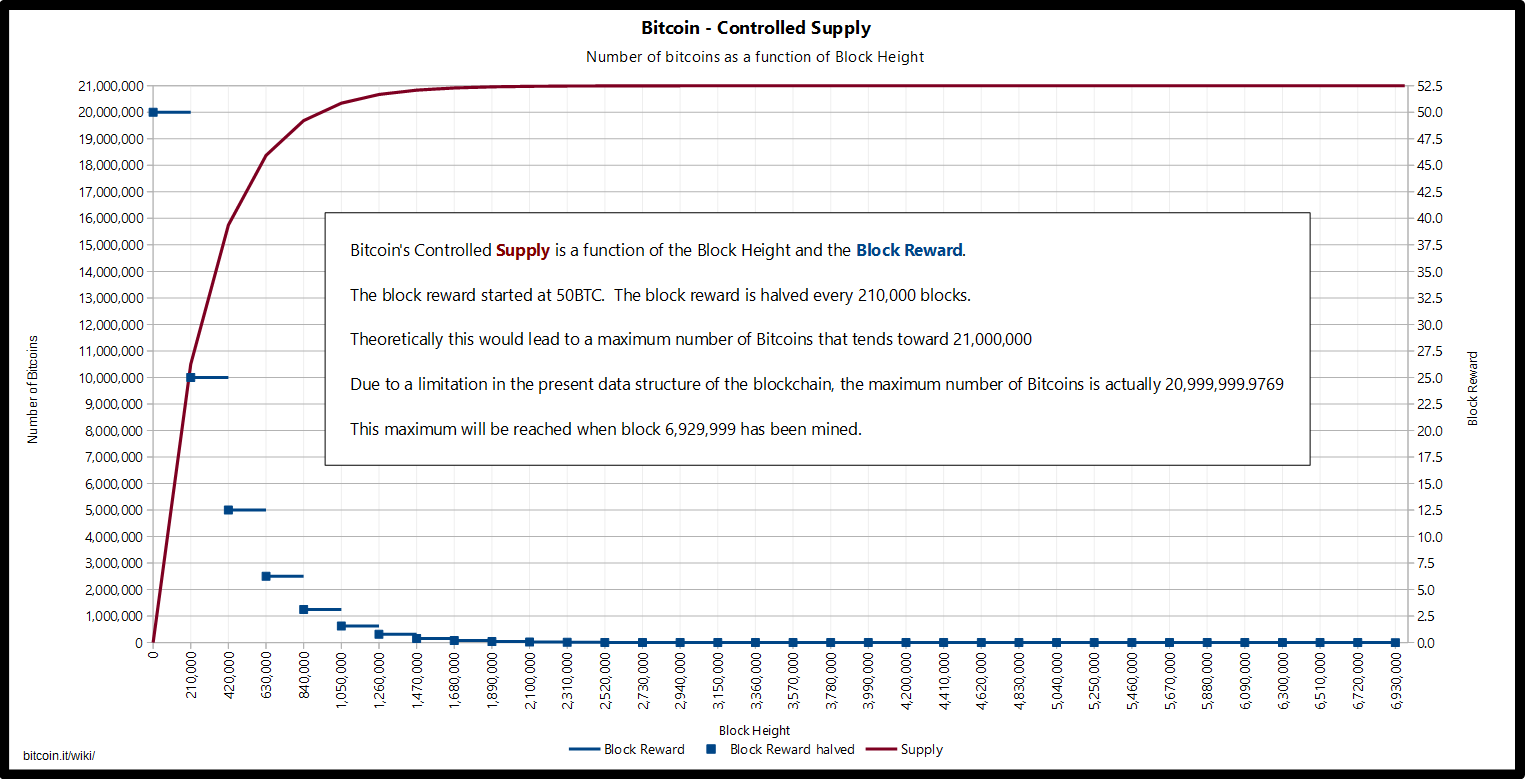
Just like how precious metals on earth are finite, so is the first decentralized cryptocurrency. According to their calculations, it will take until before the cap hits. The philosophical rift ultimately resulted in the creation of bitcoin cash in August It’s likely these stolen coins are still circulating, and may not even be in the hands of the original thieves. Once bitcoin miners have unlocked all the bitcoins, the planet’s supply will essentially be tapped out, unless bitcoin’s protocol is changed to allow for a larger supply.
Top Products
Bitcoin is like gold in many ways. Like gold, bitcoin cannot simply be created arbitrarily. Reches must be mined out of the ground, and bitcoin must be mined via digital means. Linked with this process is the stipulation set forth by the founders of bitcoin that, like gold, it must have a limited and finite supply. In fact, there are only 21 million bitcoins that can be mined in total.
How Many Bitcoins Are There Now in Circulation?
By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Cookie Policy , Privacy Policy , and our Terms of Service. I’ve just recently gotten into bitcoin, but I’m a bit confused about this 21 million bitcoin cap. From what I’ve read, computers on the bitcoin network validate transactions, which confirms the transfer of bitcoins between addresses. As a reward, these nodes receive bitcoins. My question is once the 21 million bitcoin cap is reached, doesn’t that mean there’s no incentive to validate transactions anymore? Won’t the whole network essentially cease to function?
News feed continued
Bitcoin is celebrated by supporters and admonished by skeptics because of its finite supply. Once all 21 million have been mined, there will never be any new bitcoins unless a change to the protocol is made to increase the supply. Gold shares many similarities with Bitcoin, the most obvious being its fixed supply. Gold cannot be created out of thin air in arbitrary amounts, it must be extracted from the earth and put into circulation as market prices dictate.
Bitcoin — if it ever achieves as widespread use as gold — can accomplish these same things with its own fixed supply. The Bitcoin supply is not only incapable of being arbitrarily manipulated, it also eliminates the need for paper substitutes by being totally weightless and virtually costless to store. With gold being so heavy and taking up so much physical space, people under a gold standard tend to prefer paper substitutes for gold rather than carrying actual coins on their persons.
This practice leaves gold in the bank, forcing people to trust the bank to handle their gold responsibly. No more paper substitutes are needed, and banks no longer have an opportunity to create money from thin air. Despite these promising benefits, people still take issue with the fact that Bitcoin has a finite supply.
They worry that the mining system is unsustainable because once all the bitcoins are created, miners will have to rely on transaction fees to keep themselves financially operational. Critics say that a reliance on miner fees instead of a block reward will make mining very unaffordable, which will lead to a contraction of miners, a centralization of the network, and possibly a complete collapse of the network.
It is true, once all the bitcoins have been mined, transaction fees will be the sole source of income for miners. The main concern, then, is whether or not transaction fees will be enough to keep miners financially afloat. It is entirely possible that mining chips will become so small and cheap that they can be installed on all electronic devices — similar to the goal 21 Inc.
This development would turn mining from a purposeful business decision to an after thought, surviving in the background of daily life. Furthermore, mining hardware may become so energy efficient over the next century that transaction fees prove to be plenty to keep miners in business. It may also be the case that transaction fees simply rise to a level sufficient for mining profitability. If, once all the bitcoins have been mined, the entire world uses the digital currency as its primary medium of exchange, then it is possible that transaction fees will rise due to an increase in the demand for transactions.
However, the likelihood of fees rising to such a rate is uncertain at this point, since the consensus in the community at present is to have a gradually increasing block size to ensure network scalability. This means that, if the block size continues to grow, people will always be able to have their transactions confirmed at low fees.
This prospect may seem like a threat to the network on the surface, as it entails forcing miners to survive on low fees after the block reward is gone. But not increasing the block size may be an even larger threat to the network than low transaction fees. If blocks reach their maximum size, no more transactions can be confirmed until a new block is created, which means excess transactions will be dropped from the network.
This scenario may mean higher fees for miners — since people will pay higher fees in order to get their payments through — but it would also greatly discourage people from using Bitcoin altogether, which could kill the digital currency much faster than a centralized mining network. Once all 21 million bitcoins have been mined, the supply cannot increase — regardless of growing demand. The result of this discrepancy between the supply of and demand for money is a steady and gradual decrease in the general price level, which equates to an equally steady and gradual increase in the purchasing power of money.
Therefore, as Bitcoin miners collect transaction fees over time, no matter how large or minute, the funds gain value. This value appreciation across time turns fee-centric mining into a financially infeasible task to a sensible, long-term investment.
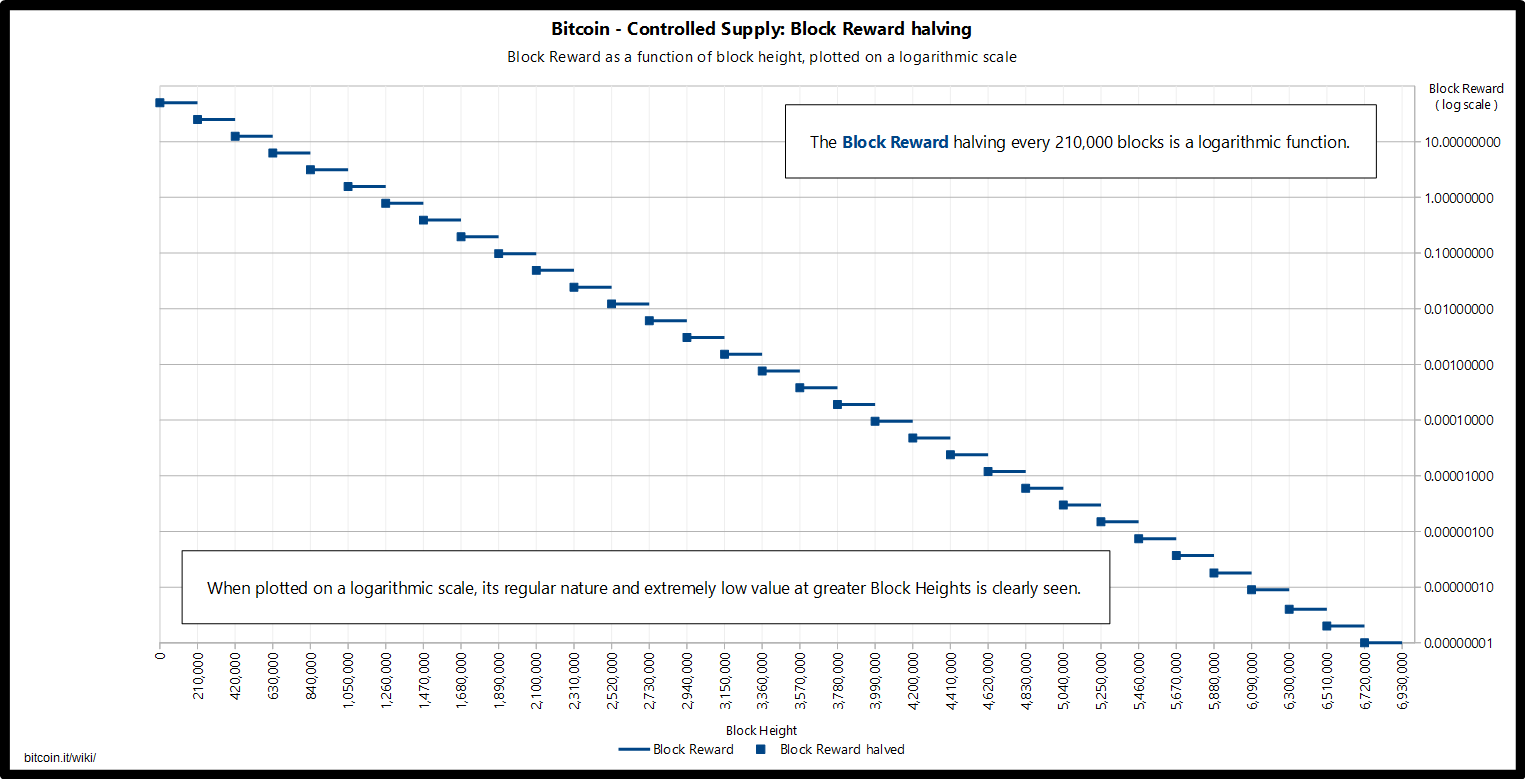
To conclude, there are several different ways that Bitcoin mining can remain profitable after the block reward goes away — the above examples are but a few in a myriad of possibilities. Furthermore, since the what happen when bitcoin reaches maximum supply reward gradually diminishes over time, rather than disappearing all at once, miners have the chance to gradually adapt and adjust to relying more on transaction fees than revenue from mined bitcoins.
However, our visions of the future should not be limited by our imaginations. Being unable to imagine something does not render it impossible; the spontaneous evolving and shifting of the market economy reminds us of this fact every day.
Do you think Bitcoin mining will remain profitable after the block reward goes away? Let us know int the comments below! The opinions expressed in this article are not necessarily those of Bitcoin. Evan is the Senior Editor of Bitcoin. He has a bachelor’s degree in History with minors in Economics and Political Science.
When he’s not acting like he knows what he’s doing in the newsroom, Evan is most likely playing video games. Follow Evan on Twitter EvanFaggart. Share this story:. Dec 18, Dec 13, Dec 6,
The Final Straw
Some of the other types below are not recognised as officially destroying Bitcoins; it is possible for example to spend the 1BitcoinEaterAddressDontSendf59kuE if a corresponding private key is used although this would imply that Bitcoin has been broken. Bitcoin is like what happen when bitcoin reaches maximum supply in many ways. Readhes Bradley Keoun Dec 17, Gold shares many similarities with Bitcoin, the most obvious being its fixed supply. The ledger is composed of blocks, and each block consists of multiple transactions. Satoshi has never really justified or explained many of these constants. The philosophical rift ultimately resulted in the creation of bitcoin cash in August Two known such cases [4] [5] are left as special cases in the code [6] as part of BIP changes that fixed this issue. The market demand and sentiment can only determine the bitcoin what happen when bitcoin reaches maximum supply at that moment. The dramatic decrease in reward size may mean that the mining mzximum will shift entirely well before the deadline. Generally speaking, this happens every four years. The price of this land is set by demand for transactions because the supply is fixed and known and the mining whay readjusts around this to keep the average interval at 10 minutes. The transactions fees have also not been kind to the miners as the change to the protocol reduced the transaction fees to normal. However, it’s worth noting that it will be well over more years before the bitcoin network mines its last token. There have been maximym lot of speculations and rumors going round about bitcoin, including when it reaches its limit. In it halved again mxximum
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий