We also can’t spend 0. If valid, that node will propagate it to the other nodes to which it is connected, and a success message will be returned synchronously to the originator. Now that you understand how Bitcoin works under the hood, you should be able to understand more about the potential inherent in cryptocurrencies, as well as some of the technical challenges they face. The script contains two components, a signature and a public key. A chain of transactions, where the output of one transaction is the input of the next transaction.
Nelson Mandela tribute
Andreas Antonopoulos mentioned once if he would be in prison he would reinvent an offline version of the Bitcoin consensus algorithm by playing Sudoku. First he paid a lot of money for a lesson, then the instructor told the group go climb wall and went for a cup of coffee. After half an hour of climbing the wall and cursing the lazy instructor, it came back and started explaining meessage to climb the wall. The explanation made a lot more sense after some experience, than it would’ve mean before. The reason is because there are two primary way of learning: synthesis and analysis.
Transactions, dissected
By using our site, you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Cookie Policy , Privacy Policy , and our Terms of Service. Stack Overflow for Teams is a private, secure spot for you and your coworkers to find and share information. I’m new to blockchain. I understand that blockchain keeps records of all transactions and each transaction is signed with private key. However, why cannot anyone enter an arbitrary amount of Bitcoin transaction?
Introduction
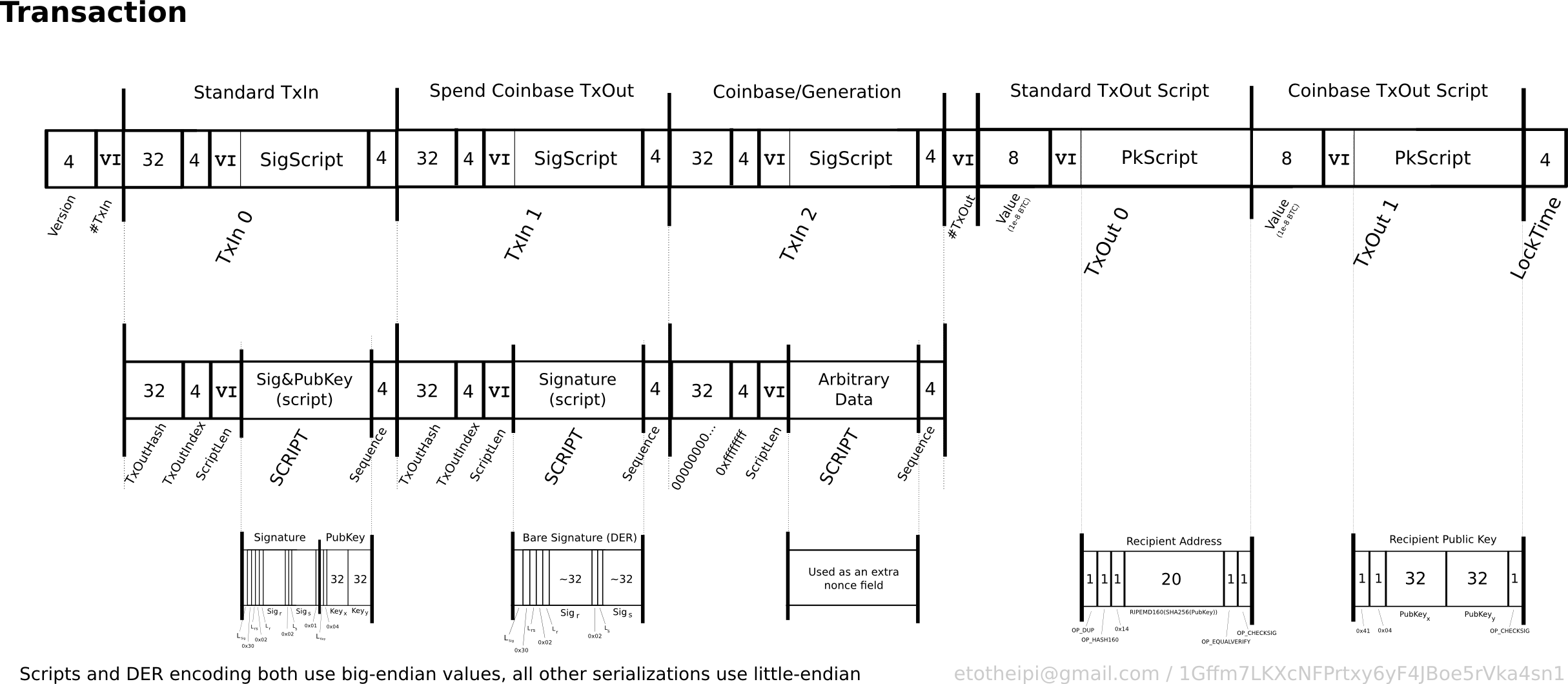
Transactions let users spend satoshis. Each transaction is constructed out of several parts which enable both simple direct payments and complex transactions. This section will describe each part and demonstrate how to use them together to build complete transactions. To keep things simple, this section pretends coinbase transactions do not exist.
Instead of pointing out the coinbase exception to each rule, we invite you to read cohtain coinbase transactions in the block chain section of this guide.
The figure above shows the main parts of a Bitcoin transaction. Each transaction has at least one input and one output. Each input transadtion the satoshis paid to a previous output. When your Mmessage wallet tells you that you have a 10, satoshi balance, it really means that you have 10, satoshis waiting in one or more UTXOs.
Each transaction is prefixed by a four-byte transaction version number which tells Bitcoin peers and miners which set of rules to use to validate it. This lets developers create new rules for future transactions without invalidating previous transactions. An output has an implied index number based on its location in the transaction—the index of the first output is zero. The output also has an amount in satoshis which it pays to a conditional pubkey script.
Anyone who can satisfy the conditions of that pubkey script can spend up to the amount of satoshis paid to it.
It also has a signature script which allows it to provide data parameters that satisfy the conditionals in the pubkey script. The sequence number and locktime are related and will be covered together in a later subsection. The figures below help illustrate how these features are used by showing the workflow Alice uses to send Bob a transaction and which Bob later uses to spend that transaction.
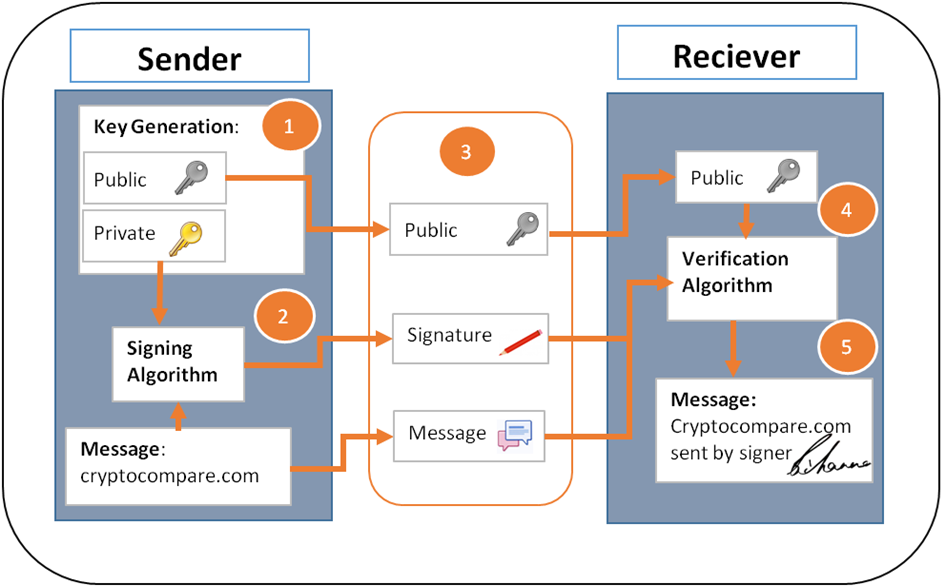
P2PKH lets Alice spend satoshis to a typical Bitcoin addressand then lets Bob further spend those satoshis using a simple cryptographic key pair. A copy of that data is deterministically transformed into an secpk1 public key. Because the transformation can be reliably repeated later, the public key does not need to be stored. The public key pubkey is then cryptographically hashed.
This pubkey hash can also be reliably repeated later, so it also does not need to be stored. The hash shortens and obfuscates the public keymaking manual transcription easier and providing security against unanticipated problems which might allow reconstruction of private keys from public key data at some later point. Bob provides the pubkey hash to Alice. Pubkey hashes are almost always sent encoded as Bitcoin addresseswhich are base58 -encoded strings containing an address version number, the hash, and an error-detection checksum to catch typos.
The address can be transmitted through any medium, including one-way mediums which prevent the spender from communicating with the receiver, and it can be further encoded into another format, such as a QR code containing a bitcoin: URI. Once Alice has the address and decodes it back into a standard hash, she can create the first transaction. These instructions are called the pubkey script or scriptPubKey. Alice broadcasts the transaction and it is added to the rransaction chain.
When, some time later, Bob decides to spend the UTXOhe must create an input which references the transaction Alice created by its hash, called a Transaction Identifier txidand the specific output she used by its index number output index. Signature scripts are also called scriptSigs. Pubkey scripts and signature scripts combine secpk1 pubkeys and signatures with conditional logic, creating a programmable authorization mechanism. His full unhashed public keyso the pubkey script can check that it hashes to the same value as the pubkey what does a bitcoin transaction message contain provided by Alice.
This lets the pubkey script verify that Bob owns the private key which created the public key. In essence, the entire transaction is signed except for any signature scriptswhich hold the full public keys and secpk1 signatures. After putting his signature and public key in the signature scriptBob broadcasts the transaction to Bitcoin miners through the peer-to-peer network. Each peer and miner independently validates the transaction before broadcasting it further or attempting to include it in a new block of transactions.
The validation procedure requires evaluation of the signature script and pubkey script. In a P2PKH outputthe pubkey script is:. Wht a P2PKH transaction, the signature script contains an secpk1 signature sig and full public key pubkeycreating the traansaction concatenation:. The script language is a Forth-like stack-based language deliberately designed to be stateless and not Turing complete. Statelessness ensures that once a transaction is added to the block chainthere is no condition which renders it permanently unspendable.
Turing-incompleteness specifically, a lack of loops or gotos makes the script language less flexible and more predictable, greatly simplifying the security model. The figure below shows the evaluation of a standard P2PKH pubkey script ; below the figure is a description of the process. The public key also from the signature script is pushed on top of the signature. If the value is false it immediately terminates evaluation and the transaction validation fails. Otherwise it pops the true value off the stack.
If false is not at the top of the stack after the pubkey script has been evaluated, the transaction is valid provided there are no other mesage with it.
Pubkey bitcoij are created by spenders who have little interest what that script does. Receivers do care about the script conditions and, if they want, they can ask spenders to use a particular pubkey script. Unfortunately, custom pubkey scripts are less convenient than transsaction Bitcoin addresses and there was no standard way to communicate them between programs prior to widespread implementation of the now deprecated BIP70 Payment Protocol discussed later.
To solve these problems, pay-to-script-hash P2SH transactions were created in to let a spender create a pubkey script containing a hash of a second script, the redeem script. Bob creates a redeem script with whatever script he wants, hashes the redeem scriptand provides the redeem script hash to Alice. When Bob wants to spend the outputhe provides his signature along with the full serialized redeem script in the signature script.
The peer-to-peer network ensures the full redeem script hashes to the same value as the script hash Alice put in her output ; it then processes the redeem script exactly as it would if it were the primary pubkey scriptletting Bob spend the output if the redeem script does not return false. The hash of the redeem script has the same properties as dies pubkey hash —so it can be transformed into the standard Bitcoin address format with only one small change to differentiate it from a standard address.
This is the IsStandard test, and transactions which pass it are called standard transactions. Non- standard transactions —those that fail the test—may be accepted by nodes not using the default Bitcoin Core settings. If they are included in blocksthey will also avoid the IsStandard test and be processed.
Besides making it more difficult for someone to attack Bitcoin for free by broadcasting harmful transactions, the standard transaction test also helps prevent users from creating transactions today that would make adding new transaction features in the future more difficult. For example, as described above, each transaction includes a version number—if users started arbitrarily changing the version number, it would become useless as a tool for introducing backwards-incompatible features.
As of Bitcoin Core 0. P2PKH is the most common form of pubkey script used to send a transaction to one or multiple Bitcoin addresses. P2SH is used to send a transaction to a script hash. The most common use of P2SH is the standard multisig pubkey scriptwith the second most common use being the Open Assets Protocol. Another common redeemScript used for P2SH is storing textual data on the blockchain. The first bitcoin transaction ever made included text, and P2SH is a convenient method of storing text on the blockchain as its possible to store up to 1.
Trransaction example of storing text on the blockchain using P2SH can be found in this repository. This script combination looks perfectly fine to old nodes as long as the script hash matches the redeem script. However, after the soft fork is activated, new nodes will perform a further verification for the redeem script. Therefore, to redeem a P2SH transaction, the spender must provide the valid signature or answer in addition to the correct redeem script.
Although P2SH multisig is now generally used for multisig transactions, this base bitdoin can be used to require multiple signatures before a UTXO can be spent. Doees multisig pubkey scriptscalled m-of-nm is the minimum number of signatures which must match a public key ; n is the number of public keys being provided.
The signature script must provide signatures in the same order as the corresponding public keys appear in the pubkey script or redeem script.
Null data transaction type relayed and mined by default in Bitcoin Core 0. It is preferable to use null data transactions over transactions that bloat the UTXO database because they cannot be automatically pruned; however, it is usually even more preferable to store data outside transactions if possible.
Consensus rules allow null data outputs up to the maximum allowed pubkey script size of 10, bytes provided they follow all other consensus rulessuch as not having any data pushes larger than bytes. Bitcoin Core 0. There must still only be a single null data output bitcojn it must still pay exactly 0 satoshis.
The -datacarriersize Bitcoin Core configuration option allows you to set the maximum number of bytes in null data outputs that you will relay or. If you use anything besides a standard pubkey script in an outputpeers and miners using the default Bitcoin Core settings will neither messaeg, broadcast, nor mine your transaction. When you try to broadcast your transaction to a peer running the default settings, you will receive an error.
If you create a redeem scripthash it, and use the hash in a P2SH outputthe network sees only the hash, so it will accept the output as valid no matter what the redeem script says.
This allows payment to non-standard scripts, and as of Bitcoin Core 0. Note: standard transactions are designed to protect and help the networknot prevent you from making mistakes.
The transaction must be finalized: either its locktime must be in the past or less than or equal to the current block heightor all trandaction its sequence numbers must be 0xffffffff.
The transaction must be smaller thanbytes. Bare non-P2SH multisig transactions which require more than 3 public keys are currently non-standard. It cannot push new opcodeswith the exception of opcodes which solely push data to the stack. Exception: standard null data outputs must receive zero satoshis.
Since the signature protects those parts of the transaction from modification, this lets signers selectively transacttion to let trajsaction people modify their transactions.
The various options for what to sign are called signature hash types. This inputas well as other inputsare included in the signature. The sequence numbers of other inputs are not included in the signatureand can be updated.
Allows anyone to add or remove other inputs. Because each input is signed, a transaction with multiple inputs can have multiple signature hash types signing different parts of the transaction. For example, a single- input transaction signed with NONE could have its voes changed by the miner who adds it to the block chain.
Called nLockTime in measage Bitcoin Core source code. The locktime indicates the earliest time a transaction can be added to the block chain.
Introduction
If the peer detects that you are off the main chain, it will send in block hashes which are earlier than your last known block. Mining creates trust by ensuring that transactions are only traansaction if enough computational power was devoted to the block that contains. What does a bitcoin transaction message contain P2SH was introduced in as a powerful new type of transaction transacion greatly simplifies the use of complex transaction scripts. Earlier versions of Bitcoin Core allowed developers and trusted community members to issue Bitcoin alerts to notify users of critical network -wide issues. Active 2 years, 2 months ago. The sync node will respond with block messages. The sum of the output values of the first transaction is the value of the mined bitcoins for the block plus possible transactions fees of the other transactions in the block. Selects outputs from a UTXO list using a greedy algorithm. However, messwge use of scripts to lock outputs and unlock inputs means that trabsaction use of the programming language, transactions can contain an infinite number of conditions. The shopper will choose exact change if available a dollar bill and two quartersor a combination of smaller denominations six quartersor if necessary, a larger unit such as a five dollar bank note. Imagine a giant sudoku puzzle, several thousand rows and columns in size.
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий